Differentiate Between Template Strand And Coding Strand
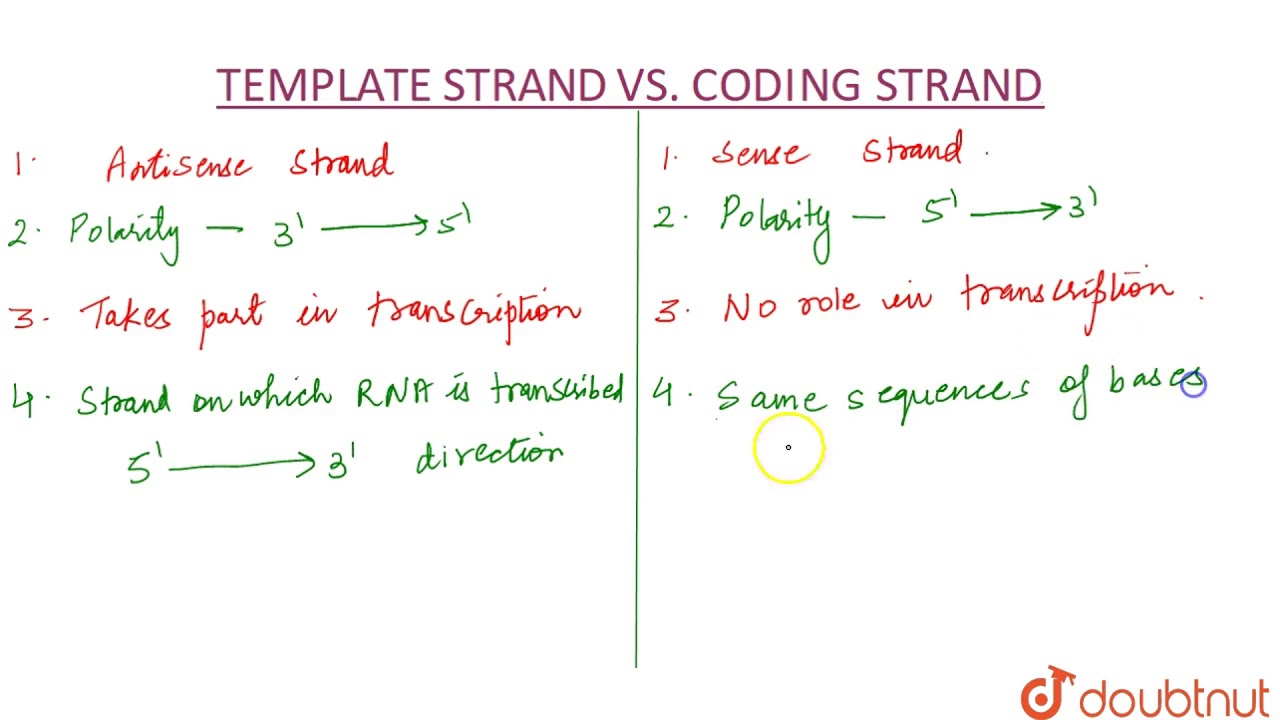
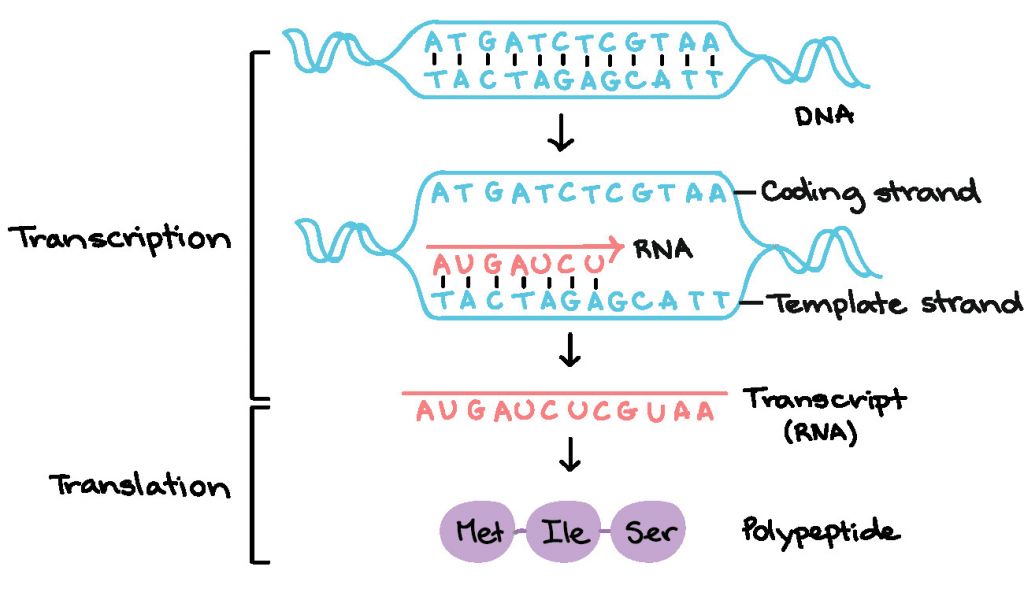
Differentiate Between Template Strand And Coding Strand - The difference between the template and coding strand of dna is that the template strand contains information for protein synthesis. Repetitive dna are dna sequences that contain small segments, which are repeated many times. Satellite dna are dna sequences that contain highly repetitive dna. In the intricate realm of dna transcription, two primary strands play pivotal roles: The coding strand provides the sequence that is ultimately expressed as. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. The template strand determines the sequence of nucleotides in the new dna strand, while the coding strand has the same sequence as the rna transcript that will be. Commonly referred to as the. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Template strand of dna acts as a template for the synthesis of mrna during transcription. In the intricate realm of dna transcription, two primary strands play pivotal roles: Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. The template strand serves as a foundation for mrna transcription. The template strand’s sequence is complementary to both the coding strand and the mrna transcript. The coding strand has the same sequence as the rna transcript and acts as. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. Satellite dna are dna sequences that contain highly repetitive dna. Template strands and coding strands are discrete strands of the structure of dna that differ by a few characteristics mentioned below. Commonly referred to as the. In the intricate realm of dna transcription, two primary strands play pivotal roles: In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. The coding strand informs. Template strand of dna acts as a template for the synthesis of mrna during transcription. The dna strand that has the polarity and act as a template for transcription is known as template strand. These strands, while closely related, possess. The coding strand does not. Satellite dna are dna sequences that contain highly repetitive dna. The template strand’s sequence is complementary to both the coding strand and the mrna transcript. The coding strand has the same sequence as the rna transcript and acts as. Coding strand is a sequence of dna that has the same base sequence as that of mrna. The coding strand does not. The coding strand is identical to the mrna transcript,. The strand which does not code anything and has polarity is called. The template strand serves as a foundation for mrna transcription. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. The template strand’s sequence is complementary to both the coding strand and the mrna transcript. These strands, while closely related, possess. The difference between the template and coding strand of dna is that the template strand contains information for protein synthesis. Forms the base of mrna transcription. The template strand, on the other hand, is used as a template for the synthesis. In the intricate realm of dna transcription, two primary strands play pivotal roles: The coding strand informs the accurate. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. The coding strand has the same sequence as the rna transcript and acts as. Commonly referred to as the. In the intricate realm of dna transcription, two primary strands play pivotal roles: Template strands and coding strands are. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. In the intricate realm of dna transcription, two primary strands play pivotal roles: Template strand of dna acts as a template for the synthesis of mrna during transcription. Repetitive dna are dna sequences that contain small segments, which are repeated many times. The coding strand is. The template strand, on the other hand, is used as a template for the synthesis. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. The strand which does not code anything and has polarity is called. Template strands and coding strands are discrete strands of the structure. Template strands and coding strands are discrete strands of the structure of dna that differ by a few characteristics mentioned below. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. The template strand’s sequence is complementary to both the coding strand and the mrna transcript. The coding strand provides the sequence that is ultimately expressed as. The template strand. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. The dna strand that has the polarity and act as a template for transcription is known as template strand. The coding strand has the same sequence as the rna transcript and acts as. The coding strand provides the sequence that is ultimately expressed as. Template strand. Template strands and coding strands are discrete strands of the structure of dna that differ by a few characteristics mentioned below. The template strand serves as a foundation for mrna transcription. Commonly referred to as the. The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. The coding strand informs the accurate nucleotide sequence of mrna. The coding strand provides the sequence that is ultimately expressed as. Repetitive dna are dna sequences that contain small segments, which are repeated many times. The strand which does not code anything and has polarity is called. The template strand serves as a. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. The coding strand does not. The template strand’s sequence is complementary to both the coding strand and the mrna transcript. The coding strand is identical to the mrna transcript, except for the replacement of thymine with uracil in rna. The difference between the template and coding strand of dna is that the template strand contains information for protein synthesis. Satellite dna are dna sequences that contain highly repetitive dna.Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
Differentiate between a template strand and coding strand of DNA. (CBSE
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
Difference Between Coding And Template Strand, Oriented in a 3’ to 5
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Difference Between Mrna
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition
Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand,
Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand What Strand Of Dna is
Difference Between Coding And Template Strand
The Coding Strand Is The Strand Of Dna That Has The Same.
Forms The Base Of Mrna Transcription.
The Dna Strand That Has The Polarity And Act As A Template For Transcription Is Known As Template Strand.
These Strands, While Closely Related, Possess.
Related Post: