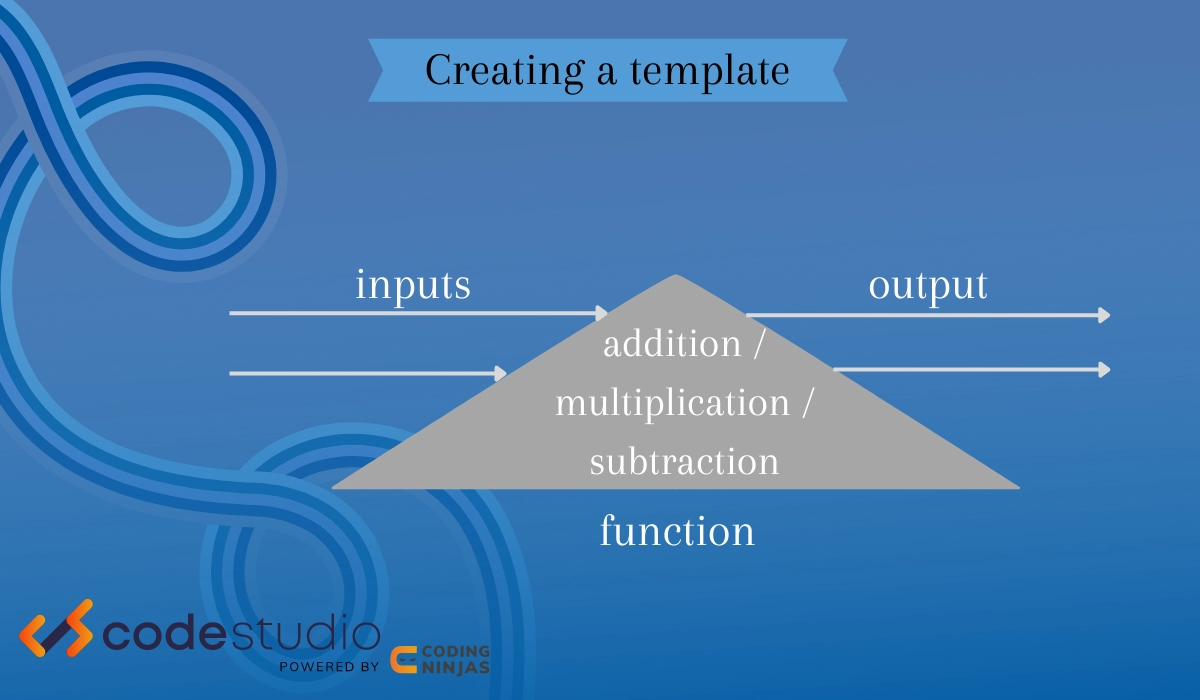
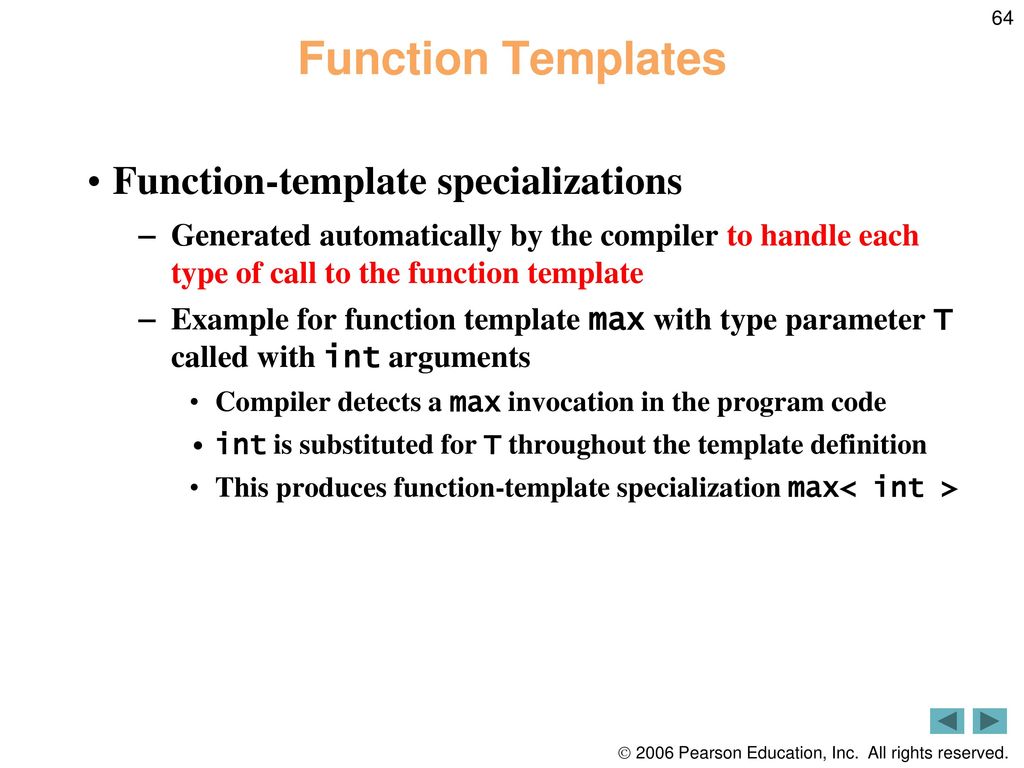
Functiontemplate Specializations
Functiontemplate Specializations - Default function arguments cannot be specified in explicit specializations of function templates, member function templates, and member functions of class templates when the class is implicitly instantiated. By default, std::swap(x, y) essentially does: These specializations allow us to provide a different implementation for a template, based on. It is possible in c++ to get a special behavior for a particular data type. What is the c++ syntax for specializing a template function that's inside a template class? This is called template specialization. Explicit template specialization (often shortened to template specialization) is a feature that allows us to explicitly define different implementations of a template for specific. To illustrate why function template specialization is important, consider the std::swap template function. An explicit specialization cannot be a friend declaration. I use the following command to compile it: With a function template, you can define special behavior for a specific type by providing an explicit specialization (override) of the function template for that type. I tried a template class definition like this: But i cannot figure out. Here i'm trying to create a method template specialization for both c and d classes using the iscord concept. If i want to specialize my function template, shouldn't i declare all my specializations in the header file? An explicit specialization cannot be a friend declaration. Default function arguments cannot be specified in explicit specializations of function templates, member function templates, and member functions of class templates when the class is implicitly instantiated. To illustrate why function template specialization is important, consider the std::swap template function. For example, consider that i have the following two classes and their usage. This is called template specialization. For example, consider that i have the following two classes and their usage. This is called template specialization. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic. These specializations allow us to provide a different implementation for a template, based on. I use the following command to compile it: If i want to specialize my function template, shouldn't i declare all my specializations in the header file? It is possible in c++ to get a special behavior for a particular data type. I tried a template class definition like this: An explicit specialization of a member function, member class or static data member of a class template shall be. These specializations allow us to provide a different implementation for a template, based on. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic. In the example code below, i have the generic function convertto and a working specialization for int, allowing me to use convertto(s) (as shown). Considering class templates, it is possible to provide template specializations for certain types. I tried a template class definition like this: Defining a function template specialization when we specialize a function template, we must supply arguments for every template parameter in the original template. Once we have a template class or function, we can create specialized versions of that template. Considering class templates, it is possible to provide template specializations for certain types. An explicit specialization of a member function, member class or static data member of a class template shall be declared in the namespace of which the class template is a member. To illustrate why function template specialization is important, consider the std::swap template function. Explicit template specialization (often shortened to template specialization) is a feature that allows us to explicitly. I tried a template class definition like this: An explicit specialization cannot be a friend declaration. In the example code below, i have the generic function convertto and a working specialization for int, allowing me to use convertto(s) (as shown). // no definitions in the original template class typedef std::valarray.</p> This is called template specialization. In the example code below, i have the generic function convertto and a working specialization for int, allowing me to use convertto(s) (as shown). By default, std::swap(x, y) essentially does: An explicit specialization of a member function, member class or static data member of a class template shall be declared in the namespace of which the class template is a. What is the c++ syntax for specializing a template function that's inside a template class? An explicit specialization cannot be a friend declaration. To illustrate why function template specialization is important, consider the std::swap template function. I use the following command to compile it: Considering class templates, it is possible to provide template specializations for certain types of groups using. What is the c++ syntax for specializing a template function that's inside a template class? But i cannot figure out. In c++ primer plus (2001, czech translation) i have found these different template specialization syntax: Default function arguments cannot be specified in explicit specializations of function templates, member function templates, and member functions of class templates when the class is. What is the c++ syntax for specializing a template function that's inside a template class? An explicit specialization of a member function, member class or static data member of a class template shall be declared in the namespace of which the class template is a member. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic. Once we have a template. What is the c++ syntax for specializing a template function that's inside a template class? For example, consider that i have the following two classes and their usage. I use the following command to compile it: If i want to specialize my function template, shouldn't i declare all my specializations in the header file? Once we have a template class or function, we can create specialized versions of that template. Considering class templates, it is possible to provide template specializations for certain types of groups using type traits and dummy enabler template parameters. In c++ primer plus (2001, czech translation) i have found these different template specialization syntax: An explicit specialization of a member function, member class or static data member of a class template shall be declared in the namespace of which the class template is a member. In the example code below, i have the generic function convertto and a working specialization for int, allowing me to use convertto(s) (as shown). This is called template specialization. But i cannot figure out. These specializations allow us to provide a different implementation for a template, based on. I tried a template class definition like this: By default, std::swap(x, y) essentially does: Here i'm trying to create a method template specialization for both c and d classes using the iscord concept. To illustrate why function template specialization is important, consider the std::swap template function.Templates (again) Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS2303, System Programming
Template specialization in C++ Coding Ninjas
Functions. ppt download
Template Function Specialization
Function Template Specialization
Function Template Specialization
Function Template Partial Specialization Is Not Allowed
PPT CS 403 Programming Languages PowerPoint Presentation, free
Function Template Specialization
Function Template Specialization
An Explicit Specialization Cannot Be A Friend Declaration.
Default Function Arguments Cannot Be Specified In Explicit Specializations Of Function Templates, Member Function Templates, And Member Functions Of Class Templates When The Class Is Implicitly Instantiated.
It Is Possible In C++ To Get A Special Behavior For A Particular Data Type.
Explicit Template Specialization (Often Shortened To Template Specialization) Is A Feature That Allows Us To Explicitly Define Different Implementations Of A Template For Specific.
Related Post: